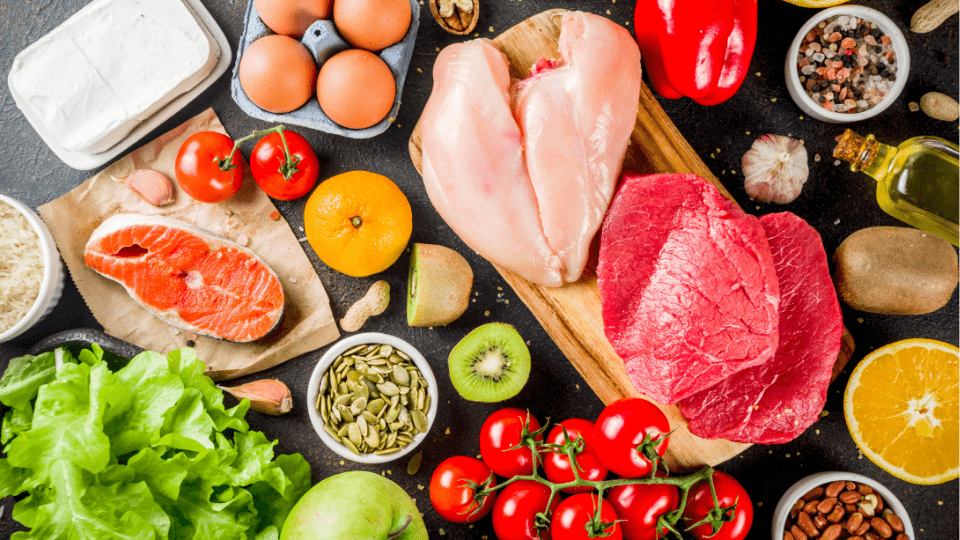
15 food that should avoid and eat
Safe 15 Foods and 15 Foods to Avoid During Pregnancy
Pregnancy is a crucial time for ensuring proper nutrition, as the health of both the mother and baby depends significantly on dietary choices. Here’s a detailed look at 15 safe foods to include in your diet and 15 foods to avoid, along with explanations for each.
Safe 15 Foods to Eat During Pregnancy
Leafy Greens
- Why: Leafy greens like spinach, kale, and Swiss chard are packed with folate, which is vital for preventing neural tube defects in the baby. They also provide iron, calcium, and fiber, which support overall health and digestion.
Lean Proteins
- Why: Lean proteins, such as chicken and turkey, offer essential amino acids necessary for the growth and repair of tissues. They are also less likely to cause digestive discomfort compared to fattier meats.
Salmon
- Why: Salmon is an excellent source of omega-3 fatty acids, which are crucial for brain and eye development in the baby. It also provides vitamin D, which aids in calcium absorption and supports bone health.
Eggs
- Why: Eggs are a complete source of protein and contain choline, which is important for brain development and reducing the risk of birth defects. They also provide a range of essential vitamins and minerals.
Sweet Potatoes
- Why: High in beta-carotene, which the body converts into vitamin A, sweet potatoes help maintain good vision and support fetal development. They are also a good source of fiber, helping to prevent constipation.
Greek Yogurt
- Why: Greek yogurt is rich in calcium, necessary for the development of the baby’s bones and teeth. It also provides protein and probiotics, which help with digestion and overall gut health.
Berries
- Why: Berries like blueberries, strawberries, and raspberries are high in antioxidants, vitamins C and K, and fiber. They help boost the immune system, improve digestion, and combat oxidative stress.
Nuts and Seeds
- Why: Nuts such as almonds and seeds like chia and flaxseeds are packed with healthy fats, protein, and fiber. They also provide essential nutrients like magnesium and vitamin E, which support overall health.
Legumes
- Why: Beans, lentils, and chickpeas are excellent sources of iron, protein, and fiber. They help prevent anemia and promote healthy digestion, reducing the risk of constipation.
Oranges
- Why: Oranges are rich in vitamin C, which enhances iron absorption and strengthens the immune system. Their high water content also helps with hydration.
Avocado
- Why: Avocados provide healthy fats that are essential for brain development. They are also high in folate, potassium, and vitamins C and K, which support overall health and help reduce leg cramps.
Whole Grains
- Why: Whole grains like brown rice, oatmeal, and whole wheat bread are rich in fiber, B vitamins, and minerals. They help regulate blood sugar levels and support digestive health.
Lean Beef
- Why: Lean beef provides a high amount of iron and protein, which are crucial for making hemoglobin and supporting the baby’s growth. Ensure it is well-cooked to avoid any foodborne illnesses.
Watermelon
- Why: Watermelon is hydrating and contains vitamins A and C, which support healthy skin and immune function. It can also help alleviate swelling and prevent dehydration.
Quinoa
- Why: Quinoa is a complete protein, providing all nine essential amino acids. It also offers iron, magnesium, and B vitamins, which are important for muscle and nerve function.
15 Foods to Avoid During Pregnancy
Raw or Undercooked Eggs
- Why: Raw or undercooked eggs can carry harmful bacteria like Salmonella, which can cause food poisoning. It’s important to cook eggs thoroughly to eliminate this risk.
Raw or Undercooked Meat
- Why: Undercooked meats can harbor bacteria such as E. coli and Salmonella, which can be harmful to both the mother and the baby. Ensure meats are cooked to a safe temperature.
Unpasteurized Dairy Products
- Why: Unpasteurized dairy products can contain Listeria, a bacteria that can cause serious infections and complications during pregnancy. Opt for pasteurized dairy products to avoid this risk.
High-Mercury Fish
- Why: Fish like shark, swordfish, and king mackerel contain high levels of mercury, which can impair fetal brain development. Choose fish lower in mercury to avoid this risk.
Deli Meats
- Why: Deli meats can be contaminated with Listeria. If consumed, they should be heated until steaming to kill any harmful bacteria and reduce the risk of infection.
Caffeine
- Why: Excessive caffeine intake can increase the risk of miscarriage and affect fetal development. Limiting caffeine to 200-300 mg per day is generally recommended.
Alcohol
- Why: Alcohol can lead to fetal alcohol spectrum disorders, affecting the baby’s brain and physical development. No amount of alcohol is considered safe during pregnancy.
Raw Sprouts
- Why: Raw sprouts, including alfalfa and bean sprouts, can be contaminated with bacteria like Salmonella or E. coli. Cooking sprouts can help reduce this risk.
Soft Cheeses
- Why: Soft cheeses like Brie and Camembert, unless labeled as pasteurized, can carry Listeria. These cheeses should be avoided unless thoroughly cooked.
High-Sugar Foods
- Why: Foods high in sugar can lead to gestational diabetes and contribute to excessive weight gain. It’s best to limit intake of sugary snacks and beverages.
Processed Junk Foods
- Why: Junk foods often contain unhealthy fats, excessive sugars, and high levels of sodium. They can negatively impact overall health and pregnancy outcomes.
Artificial Sweeteners
- Why: Some artificial sweeteners, like saccharin, can cross the placenta and may not be safe. It’s better to use natural sweeteners in moderation or consult a healthcare provider.
Unwashed Fruits and Vegetables
- Why: Unwashed produce can carry harmful bacteria or parasites. Always wash fruits and vegetables thoroughly to reduce the risk of foodborne illnesses.
Certain Herbal Teas
- Why: Some herbal teas can trigger contractions or other complications. Consult with a healthcare provider before consuming any herbal teas during pregnancy.
Excessive Salt
- Why: High sodium intake can lead to increased blood pressure and swelling. Opt for low-sodium options to maintain healthy blood pressure levels and reduce fluid retention.
Conclusion
Navigating dietary choices during pregnancy can be challenging, but making informed decisions about what to eat and avoid is crucial for ensuring a healthy pregnancy. Incorporating nutrient-dense foods while avoiding potentially harmful items can contribute significantly to both maternal and fetal health. Always consult with a healthcare provider for personalized dietary advice tailored to your specific needs and conditions.